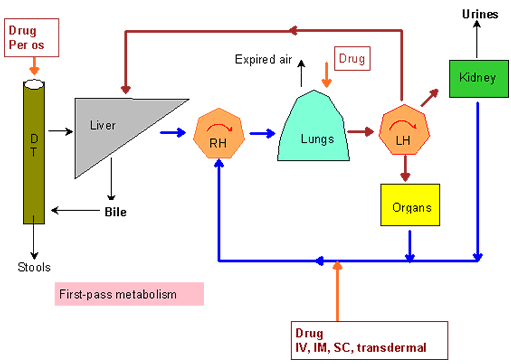
Introduction: Route of administration is an important factor that influences the absorption of a drug. The interval between administration and onset of action is determined administration. Biological lag is the interval of a drug and development of response.
Classification of routes: The routes of drug administration may be classifies as:
Oral or even enteral route: It is most generally used route with regard to drug administration.
Advantages of oral route:
1. It is a safe, convenient and economical route.
2. Self medication is possible.
3. Withdrawal of those drug is possible.
Disadvantages of oral route:
1. Onset of drug action is slow.
2. Drugs that are bitter in taste can't become administered.
3. Drugs making nausea and vomiting cannot become administered.
4. The drug can easily end up being inactivated by gastric enzymes.
5. This route is not not possible in an unconscious patient.
Enteric coated pills and tablets: These types of are oral preparations coated with cellulose acetate or perhaps gluten. These kinds of coatings cannot become destroyed by the acid juice of those stomach. Only the alkaline intestinal juice removes these types of coatings. So inactivation of these the drug in the stomach is avoided. Thus a desired concentration of these drug is released in the intestine.
Sustained release or perhaps time release preparations (Spansules): These are oral preparations containing various coatings. Each coating dissolves at different time intervals releasing the lively drug. So the drug is released slowed for prolonged periods.
Parenteral routes: Routes of administration other compared to oral (enteral) route are termed as parenteral.
Advantages of parenteral route:
1. Absorption is rapid and quick.
2. Accurate dose of the the drug can easily be given.
3. The drug enters into circulation in an lively form.
4. It is useful in emergency.
5. It is useful in case of an unconscious patient.
Disadvantages of parenteral route:
1. Pain can easily be created by injection.
2. Abscess procedures are required for injection.
3. Sterile procedures are required for injection.
4. It is an highpriced route.
5. Self medication just isnt not possible.
a. Injection
1. Intradermal: The drug is injected in the layers of skin e.g. B.C.G vaccine.
2. Subcutaneous: Non-irritant substance alone can also be become injected by this kind of route. The rate of absorption is even and slow and hence the effect is prolonged.
3. Intramuscular: The drug is injected deep into muscle tissue. The rate of absorption is uniform and onset of action is rapid.
4. Intravenous: A drug is directly injected into a vein.
Advantages:
(i) The drug enters into circulation in an lively form.
(ii) Desired blood concentration may also be end up being obtained.
(iii) Quick and immediate response is produced.
(iv) It is useful in case of emergency.
(v) It is useful in an unconscious patient.
Disadvantages:
(i) Drugs which precipitate blood constituents cannot become administered.
(ii) Untoward reactions, if occur are immediate.
(iii) Withdrawal of the drug is not possible.
5. Intra-arterial: In this kind of route, a drug is injected into an artery. The effect of a drug can also be become localized in a particular organ or perhaps tissue by choosing the appropriate artery. Anticancer drugs are sometimes administered by this kind of route.
6. Intraperitoneal: In this kind of route, a drug is injected into the peritoneal cavity. By this, fluid such as glucose and saline can easily be given to children.
7. Bone - marrow: Bone marrow injection is very really just like to intravenous injection. This kind of route is useful when veins are not available due to circulatory collapse or perhaps thrombosis. In adults, the sternum is chosen and in kids, tibia or perhaps femur is chosen for injection.
b. Inhalation: Gases, volatile liquids, aerosols or even vapours can be become administered by this kind of route.
Advantages:
1. Immediate absorption of those drug.
2. Localization of the reaction in diseases of the the respiratory tract.
Disadvantages:
1. Poor ability to regulate the dose.
2. Local irritation of these respiratory tract can easily increase its secretions.
3. Difficulty in the method of administration.
c. Transacutaneous route: It is further classified as
i) Iontophoresis
ii) Inunctions
iii) Jet injection
iv) Adhesive units.
i) Iontophoresis: In this particular method, a drug is driven deep into the skin by means of a galvanic current e.g. salicylates. Anode iontophoresis is used regarding positively charged drugs and cathode iontophoresis is use with regard to contrarily charged compounds.
ii) Inunction: It is rubbing the drug on the skin. The drug gets absorbed and produces systemic reaction e.g. nitroglycerine ointment for angina.
iii) Jet injection: This kind of method does not require a a spring. So it is painless. Using a gun such as instrument with a micro-fine orifice, the drug solution is projected as a a high velocity jet (dermojet). The drug solution passes through superficial layers of skin and gets deposited in the subcutaneous tissue. This method is useful with regard to mass inoculation.
iv) Adhesive units: It is a trans-dermal drug delivery system. It is available in the form of adhesive unit. It delivers the drug slowly. So it produces prolonged systemic response. e.g. scopolamine regarding motion sickness.
d. Transmucosal route: It is further classified as
A) Sub-lingual
B) Trans-nasal
C) Trans-rectal.
A) Sub-lingual route: A tablet containing the drug is put under the tongue and allowed to dissolve in the mouth e.g. nitroglycerine and isoprenaline.
Advantages of sub-lingual route:
1. Rapid onset of action.
2. Termination of those the response by spitting the tablet.
3. Inactivation of the the drug in the stomach is avoided.
4. The drug enters directly into systemic circulation without inactivation in the liver.
B) Trans-nasal route: It is useful regarding drugs in the form of snuff or perhaps nasal spray. The drug is readily absorbed through the mucous membrane of nose. e.g. posterior pituitary powder.
C) Trans-rectal route: Drugs may also be become absorbed through the rectum for creating systemic effects. e.g. aminophylline with regard to broncho-spasm, diazepam regarding status epileptic-us. Advantages of rectal route are:
1. Gastric irritation is avoided.
2. It is useful in old and terminally ill patients.
e. New drug delivery systems:
i) Occusert: It is placed directly under the eyelid. It can release drugs like pilocarpine with regard to prolonged periods.
ii) Progestasert: It is an intrauterine contraceptive device. It produces controlled release of progesterone within the uterus regarding a year.
iii) Pro-drug: It is an inactive drug which after administration is metabolized into an active drug. For example, I-dopa is an inactive compound. After administration, it is metabolized for the the energetic drug dopamine which is is effective in Parkinson.
Local application: Drugs in the form of powder, paste, lotion, drops and ointment can end up being applied locally for action at the site of application. Drugs can be become applied on mucous membranes of nose, conjunctiva, vagina, urethra and rectum. The following are some preparations which are meant regarding local application:
1. Bougie with regard to urethra.
2. Pessary with regard to vagina.
3. Suppository with regard to vagina and rectum.
4. Enemata with regard to rectum.